InstaDeep, the AI company behind DeepChain™, is a proud sponsor of UmojaHack Africa 2021, Africa’s biggest inter-university machine learning hackathon, alongside DeepMind, Microsoft and NVIDIA. This year, DeepChainTM is powering an antibody classification challenge asking participants from more than 120 universities to help develop a better treatment against future influenza pandemics.
UmojaHack Africa is back for its second year following a successful premiere in 2020! The hackathon, which runs on the Zindi.Africa platform on March 27th and 28th features three tracks from beginner level to advanced, and InstaDeep is proud to bring this years’ advanced track with the theme of Bioinformatics leveraging InstaDeep’s new breakthrough innovation, DeepChainTM, an AI-powered protein design platform that supports protein drug discovery, accelerating new protein design and lead candidates optimization, with the goal of maximizing confidence and success rate in developing protein-based drugs.
Develop a better treatment to combat future influenza
The track titled ‘DeepChain Antibody Classification Challenge’ leverages InstaDeep’s revolutionary new AI-powered platform, DeepChain™, which uses deep learning to model protein interactions to help design better drugs. One of the things it can be used for is to evaluate the effectiveness of neutralizing antibodies against viruses like COVID-19 and influenza. Therefore, in this challenge, we are asking participating students to help develop a better treatment to combat future influenza pandemics.
Our goal is to design a type of protein that we generally call a neutralising antibody that will effectively target the viral micro-organism, solidly binding to the influenza virus, rendering it inactive and preventing it from infecting cells, which will offer enormous therapeutic potential and help save lives!
Using DeepChainTM to explore the interaction between the influenza virus and a neutralizing antibody
The influenza virus uses a protein called haemagglutinin (HA), located on its external shell, to attach to receptor proteins present on specialised cells in your throat, nose and/or lungs. Like a key and lock combination, the interaction between these two proteins facilitates the entry of the virus into the human cells. From there, the newly infected cell goes on to cause an immune reaction, usually resulting in the cell’s death.
How can we block this infection? Antibodies!
The scientific community has been working to produce and study neutralizing antibodies targeting influenza for years now. Taking their work forward, we can now use DeepChainTM and the power of AI to accelerate this process.
As a sneak peek of the challenge, we have loaded an antibody-HA complex example to DeepChainTM. The example used contains the influenza H3N2 virus haemagglutinin (HA) complexed with a neutralising antibody and you can find it through its PDB ID: 2VIR. With DeepChainTM we can easily identify the positions in the antibody that are in close contact with the viral HA protein. These are known as the Complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) and are key to the challenge when designing better, more effective antibodies.
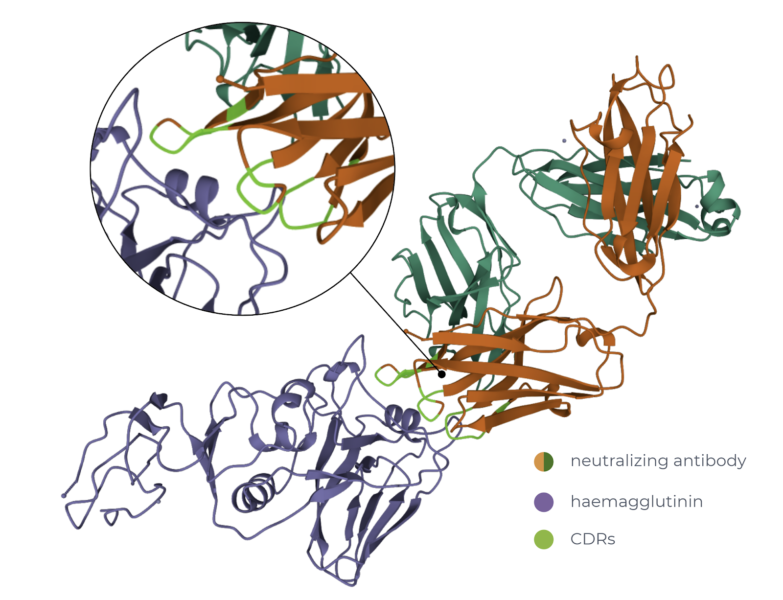
Legend: Cartoon representation of HA protein from the Influenza H3N2 variant (purple) in complex with a neutralizing antibody (orange and green) with a zoom-in depicting the interface (light green) between the two. Screenshot taken from DeepChainTM. PDB ID:2VIR
We now ask for you to leverage DeepChainTM to optimize the interaction between these two proteins to generate the most efficient antibody there is! To learn how check the challenge page.
So why the flu?
Influenza pandemics occur when a new flu virus can infect people and spread globally, and the World Health Organization estimates that between 230-650,000 die of influenza related-causes worldwide every year (1). The Spanish Influenza pandemic of 1918 infected over 500M people, a third of the world population back then, about four times as many as the current COVID-19 pandemic.
We now use preventive measures to try and prevent such a catastrophe, in the form of annual vaccines. However, influenza’s genetic makeup is constantly evolving and mutating, preventing one single vaccine from being effective. Recently the H3N2 variant has been shown to have dangerous pandemic potential, and a possible co-infection with influenza and COVID-19 could carry even higher risks. For this reason, we need neutralising antibodies that can target any new flu variant that might escape current vaccines’ protection. As opposed to a vaccine, these would constitute a therapeutic option for patients who are already infected, preventing the virus from spreading and essentially, stalling and defeating the infection.
Using DeepChainTM, we can score the effectiveness of an influenza-binding antibody. All we need is a starting antibody sequence, and that’s where you come in!
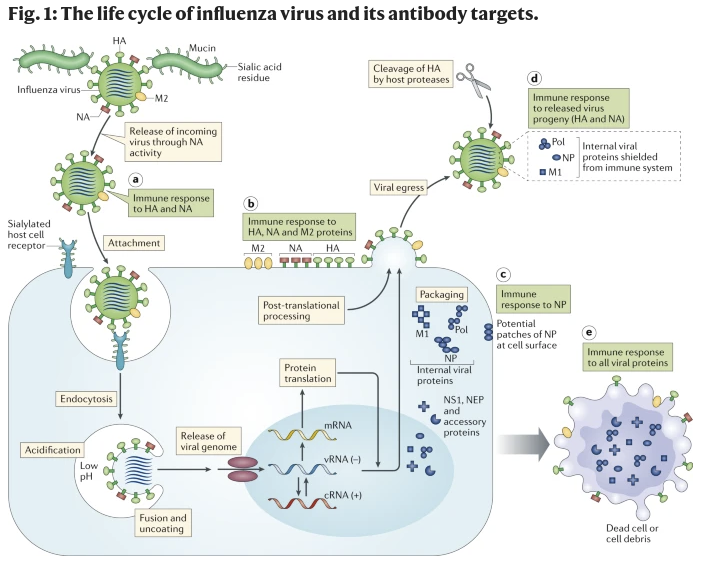
Nat Rev Immunol 19, 383–397 (2019)(2)
So what do I have to do to participate?
The event is restricted to the participating universities, so firstly make sure your university is amongst the more than 120 universities across 21 countries that have enrolled! Then log in using your university code and add your university to your profile. You then select the track you want to participate in and after this, you are ready to start practising and prepare your team for UmojaHack. All the information you need can be found on the challenge page.
Game-changing event
In addition to creating the biotechnology challenge, InstaDeep is proud to feature as a main sponsor of the event alongside tech leaders such as Microsoft, DeepMind, NVIDIA, Standard Bank, and Old Mutual.
“We are delighted to support UmojaHack Africa again, an incredible initiative close to our hearts. Seeing students from more than 120 universities come together to collaborate on real-world Machine Learning challenges is truly inspiring. This is in our opinion the best way to accelerate AI growth on the continent. Hackathons like UmojaHack bring us one step closer to achieving InstaDeep’s mission: building an AI-First world that benefits everyone”, says Karim Beguir, Co-Founder and CEO of InstaDeep.
According to the organisers, UmojaHack is about building skills, creating new machine learning applications to solve real-world problems, and forging new connections among the students as well as with the industry.
“UmojaHack Africa has proven to be a game-changing event, especially when so many young people have been impacted by the global pandemic. This is a chance for students from across the continent to come together to learn, compete, and have fun,” says Celina Lee, CEO of Zindi in a press release. “We are incredibly excited to see what the students come up with in just one weekend.”
The event will be broadcasted live on Zindi’s YouTube channel and on umojahack.africa.
Fancy a DeepChainTM live demo?
The DeepChain™ Playground module leverages transformer algorithms and is now accessible for free to analyse your protein sequences of interest and to discover variants and key regions. Learn what you can do with it on our blog ‘AI Language Models Offer a Novel Approach to Protein Sequence Exploration’
Create your personalised and secure account and start using AI to accelerate and improve your design process leading to key discoveries by registering here.
To learn more about DeepChain™, feel free to send us an email at hello@deepchain.bio!
If you are a computational biologist passionate about AI, please consider joining our team! You can find our job offers for a biology-based position here.
References:


